CB-RISE: Improving the RISE Interpretability Method Through Convergence Detection and Blurred Perturbations
Abstract
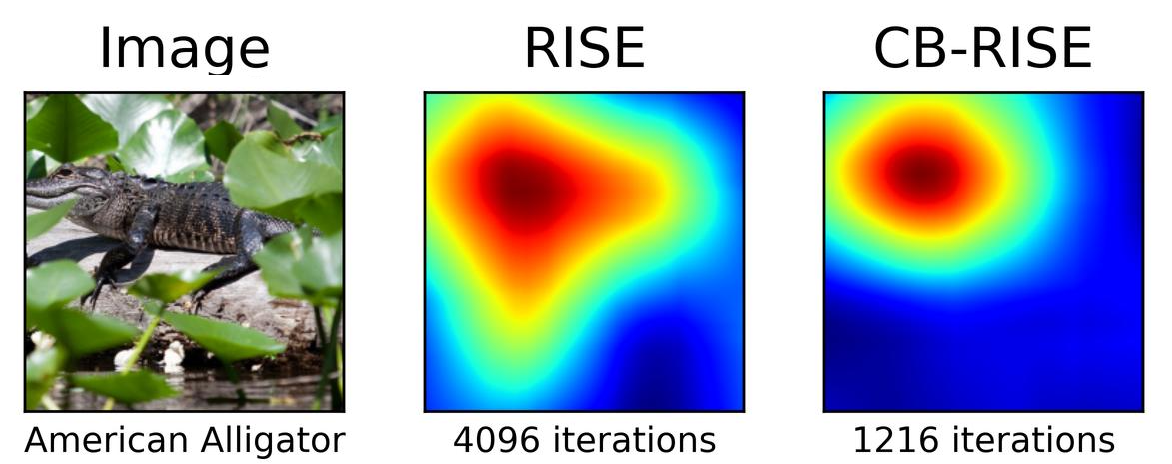
This paper presents significant advancements in the RISE (Randomized Input Sampling for Explanation) algorithm, a popular black-box interpretability method for image data. RISE’s main weakness lies on the large number of model evaluations required to produce the importance heatmap. Furthermore, RISE’s strategy of occluding image regions with black patches is not advisable, as it may lead to unexpected predictions. Therefore, we introduce two new versions of the algorithm, C-RISE and CB-RISE, each incorporating novel features to address the two major challenges of the original implementation. C-RISE introduces a convergence detection based on the Welford algorithm which reduces the computational burden of the algorithm by ceasing computations once the importance map stabilizes. CB-RISE, additionally, introduces the use of blurred masks as perturbations, equivalent to applying Gaussian noise, as opposed to black patches. This allows for a more nuanced representation of the model’s decision-making process. Our experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of these improvements, successfully enhancing the effectiveness of the generated heatmaps while improving their quality, qualitatively, and showing a speedup of approximately 3.
Citation
@inproceedings{stanchi2024cb,
title={CB-RISE: Improving the RISE Interpretability Method Through Convergence Detection and Blurred Perturbations},
author={Stanchi, Oscar and Ronchetti, Franco and Bianco, Pedro Dal and Rios, Gast{\'o}n and Ahon, Santiago Ponte and Hasperu{\'e}, Waldo and Quiroga, Facundo},
booktitle={Conference on Cloud Computing, Big Data \& Emerging Topics},
pages={45--58},
year={2024},
organization={Springer}
}